As shown in our resultsall classification methods achieved very good results. However, as reported in several studies, SVM and predictive methods have some limitations, since they could lead to too optimistic statement. Meyer et al.compared SVM to several other classification and regression methods, by means of standard performance measures. This comparison showed that all predictive methods have good performances, and SVM did not demonstrate its overall superiority. Parikesit et al.and Smith et al.assessed different predictive methods applied to gene annotations, and reported that predictions should be chosen carefully in order to avoid introducing biases. Although validation is necessary in independent wet lab experiments, the new genomic features identified in our work shed new light on the biology underlying histological grade in breast cancer, as evidenced in the following section. Among its possible Cinoxacin target genes, clusterinis a pro-proliferative gene and one of the genes induced by exposure to ionizing radiation, which usually causes oxidative damage, 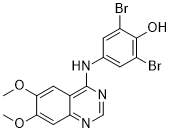 while neurobeachin, a lysosomal-trafficking regulator, is one of the genes of the common fragile site regions. Class 1 comprises also Hsa-miR-515-5p, that is usually down-regulated by estrogen receptor in BC. In our case this miRNA in unexpectedly up-regulated; this may possibly due to the fact that our database contains both ER+ and ER- BC samples. Hsa-miR-515-5p regulates a growth factor signalling transducer, the ring finger protein-like 1, which has a role in growth control of BC cell line. In class 1 we found also Hsa-miR-142-3p, that, with Hsa-miR-532-5p, is a circulating miRNA already considered biomarker of colorectal carcinoma. Two possible targets of this miRNAs are fibronectin type III domain containing 3A, whose expression controls cell adhesion, migration and proliferationand myotubularin related protein 9, whose chromosomal gain is considered a prognostic event in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The last gene is also a possible target of Hsa-miR-941, that is a circulating biomarker of ulcerative colitis. Hsa-miR-455-5p has already been found to be up-regulated in different types of tumors, as basal cell carcinoma of the skin, endometrial adenocarcinomas, but it also has a diagnostic value in laryngeal cancerand in hepatocellular adenoma. Its target tight junction protein 1, being a protein of the cytoplasmic membrane surface of intracellular tight junction, could have a role in communication among two cells by cell-cell junction. A role for TJP1 in controlling epithelial cell integrity in BC cells has been pointed out. It is not a coincidence to find in G3 BC several upregulated miRNAs common to melanoma, as Axelsen JB et al.reported that the genes selectively altered in BC majorly overlap with the ones altered in melanoma. A combination of genetic and epigenetic Anemarsaponin-BIII changes has been shown to contribute to development of human cancer resulting in deregulation of gene expression and function. Genetic changes result in widespread deregulation of gene expression profiles and the disruption of signaling networks that control normal cell proliferation and functions. In addition to changes in DNA and chromosomes, oncogenic processes can be profoundly influenced by epigenetic mechanisms.
while neurobeachin, a lysosomal-trafficking regulator, is one of the genes of the common fragile site regions. Class 1 comprises also Hsa-miR-515-5p, that is usually down-regulated by estrogen receptor in BC. In our case this miRNA in unexpectedly up-regulated; this may possibly due to the fact that our database contains both ER+ and ER- BC samples. Hsa-miR-515-5p regulates a growth factor signalling transducer, the ring finger protein-like 1, which has a role in growth control of BC cell line. In class 1 we found also Hsa-miR-142-3p, that, with Hsa-miR-532-5p, is a circulating miRNA already considered biomarker of colorectal carcinoma. Two possible targets of this miRNAs are fibronectin type III domain containing 3A, whose expression controls cell adhesion, migration and proliferationand myotubularin related protein 9, whose chromosomal gain is considered a prognostic event in oesophageal adenocarcinoma. The last gene is also a possible target of Hsa-miR-941, that is a circulating biomarker of ulcerative colitis. Hsa-miR-455-5p has already been found to be up-regulated in different types of tumors, as basal cell carcinoma of the skin, endometrial adenocarcinomas, but it also has a diagnostic value in laryngeal cancerand in hepatocellular adenoma. Its target tight junction protein 1, being a protein of the cytoplasmic membrane surface of intracellular tight junction, could have a role in communication among two cells by cell-cell junction. A role for TJP1 in controlling epithelial cell integrity in BC cells has been pointed out. It is not a coincidence to find in G3 BC several upregulated miRNAs common to melanoma, as Axelsen JB et al.reported that the genes selectively altered in BC majorly overlap with the ones altered in melanoma. A combination of genetic and epigenetic Anemarsaponin-BIII changes has been shown to contribute to development of human cancer resulting in deregulation of gene expression and function. Genetic changes result in widespread deregulation of gene expression profiles and the disruption of signaling networks that control normal cell proliferation and functions. In addition to changes in DNA and chromosomes, oncogenic processes can be profoundly influenced by epigenetic mechanisms.
Monthly Archives: April 2019
The incidence of hip fractures and cost for treatment will rise in the novel proofs to enhance the current classification
Tree shrew is a small mammal which closer to human in phylogenetically relationship than other small experimental animals, such as mouse, rat, rabbit and guinea pig; and farther to human than chimpanzee, monkey, and pig. We also verified the cDNA sequence of tsGAPDH using qRT-PCR and verified the protein expression of tsGAPDH with western blot. Tree shrew has small body size, relative low cost and relatively easy to use in 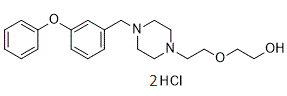 the laboratories. Currently, tree shrew is classified as Scandentia, that is between Primates and Insectivora, though the very early studies suggest that the tree shrew has been grouped into the Primates. Our phylogenetic analysis supports the current classification for tree shrew. The phylogenetic relationship of tree shrew and human is closer than mouse, rat, guinea pig and rabbit. Thus, tree shrew can be used to closely mimic human disorders than use of mouse, rat, guinea pig or rabbit. The difference of GAPDH in amino acid’s number between tree shrew and human is small. The number is only 17 of total 333 amino acids. We tried to analyze the cDNA sequence of tsGAPDH to find the tree shrew special sites but failed. Lack of tree shrew genome database and without well-understanding of the tree shrew genome, it was difficult to learn more genetic information based on only a cDNA sequence of housekeeping gene and a few genome information. Although it is enough to apply tsGAPDH as an internal reference in study with the tree shrew as experimental animal model. GAPDH has been considered as a housekeeping gene in human, mouse, rat or other experimental animals. GAPDH is widely used as an internal reference in quantitative methods, including qRT-PCR, western blot, which are two popularly ones used to Butenafine hydrochloride quantify RNA and protein content, respectively. In this study, tsGAPDH was verified that it widely and richly exists in each examined tissue of tree shrew by both qRT-PCR and western bolt. The tsGAPDH still can be measured even the sample was loaded in small quantity of 5 mg total protein by western blot; and if the quantity of total protein loading was more than 25 mg, it was difficult to analyze the difference between various tissues. But tsGAPDH was not expressed at an equal level in every tissue and it is not expressed in complete parallel level of RNA and protein. In our data, tsGAPDH expressed in a significantly high level of RNA in skin among all measured tissues. Expression of tsGAPDH in muscle was lower than that in skin; and expression in kidney was lower than that in muscle. The RNA expressions in other tissueswere lower than that in kidney, and they were roughly equal between each other. The expression of tsGAPDH protein was different to RNA’s. The tsGAPDH protein expressed in a high level in muscle, bladder, kidney, skin, spleen and brain. The liver and intestine had relatively lower content of tsGAPDH protein. In brief, tree Amikacin hydrate shrew’s muscle, kidney and skin had relatively high GAPDH expression level in both RNA and protein. The tissue preference of tsGAPDH maybe deserve more further works. Osteoporosis is associated with deficiency of ovarian hormone following menopause. A sharp decrease in ovarian estrogen production is the predominant cause of rapid, hormone-related bone loss after menopauseas a result of higher bone turnover, an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption & net bone loss. The common sites of fracture among postmenopausal women include the vertebrae, forearm and hip.
the laboratories. Currently, tree shrew is classified as Scandentia, that is between Primates and Insectivora, though the very early studies suggest that the tree shrew has been grouped into the Primates. Our phylogenetic analysis supports the current classification for tree shrew. The phylogenetic relationship of tree shrew and human is closer than mouse, rat, guinea pig and rabbit. Thus, tree shrew can be used to closely mimic human disorders than use of mouse, rat, guinea pig or rabbit. The difference of GAPDH in amino acid’s number between tree shrew and human is small. The number is only 17 of total 333 amino acids. We tried to analyze the cDNA sequence of tsGAPDH to find the tree shrew special sites but failed. Lack of tree shrew genome database and without well-understanding of the tree shrew genome, it was difficult to learn more genetic information based on only a cDNA sequence of housekeeping gene and a few genome information. Although it is enough to apply tsGAPDH as an internal reference in study with the tree shrew as experimental animal model. GAPDH has been considered as a housekeeping gene in human, mouse, rat or other experimental animals. GAPDH is widely used as an internal reference in quantitative methods, including qRT-PCR, western blot, which are two popularly ones used to Butenafine hydrochloride quantify RNA and protein content, respectively. In this study, tsGAPDH was verified that it widely and richly exists in each examined tissue of tree shrew by both qRT-PCR and western bolt. The tsGAPDH still can be measured even the sample was loaded in small quantity of 5 mg total protein by western blot; and if the quantity of total protein loading was more than 25 mg, it was difficult to analyze the difference between various tissues. But tsGAPDH was not expressed at an equal level in every tissue and it is not expressed in complete parallel level of RNA and protein. In our data, tsGAPDH expressed in a significantly high level of RNA in skin among all measured tissues. Expression of tsGAPDH in muscle was lower than that in skin; and expression in kidney was lower than that in muscle. The RNA expressions in other tissueswere lower than that in kidney, and they were roughly equal between each other. The expression of tsGAPDH protein was different to RNA’s. The tsGAPDH protein expressed in a high level in muscle, bladder, kidney, skin, spleen and brain. The liver and intestine had relatively lower content of tsGAPDH protein. In brief, tree Amikacin hydrate shrew’s muscle, kidney and skin had relatively high GAPDH expression level in both RNA and protein. The tissue preference of tsGAPDH maybe deserve more further works. Osteoporosis is associated with deficiency of ovarian hormone following menopause. A sharp decrease in ovarian estrogen production is the predominant cause of rapid, hormone-related bone loss after menopauseas a result of higher bone turnover, an imbalance between bone formation and bone resorption & net bone loss. The common sites of fracture among postmenopausal women include the vertebrae, forearm and hip.
cDNA sequence and performed evolution and sequence analysis base on GAPDH sequences
The number of Amikacin hydrate literatures which tree shrews are used as an experimental animal model in amount of disease is increasing, because of their well-developed visual system, higher-ratio of brain to body mass, or infection of speciesespecially pathogens, such as hepatitis virus and influenza virus. Currently, tree shrew models are mainly used for research into the nervous, visual systems, and viral infection disease. However, only a few tree shrew genes have the full-length sequences. In the Genbank database, there are only around 200 molecules with coding information. Moreover, there are only a few antibodies and detecting kits available for studying tree shrew. It is difficult to detect and characterize gene and protein expression profile without Povidone iodine sequence information and species-especially antibodies. Due to those reasons, it is narrow the wide application of tree shrew as a model for diseases’ mechanism research. Housekeeping gene is a group of typically constitutive genes that are required for the maintenance of basic cellular function. Some housekeeping genes are expressed at relatively constant levels in most physiological situations; others may vary according to experimental conditions. Therefore, housekeeping genes are generally used as internal reference to normalize target genes in many examine methods, such as quantitative real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, western immunoblotting, immunohistochemistry, and so on. An ideal housekeeping gene as internal reference should be widely stably expressed within all cells of an organism under normal and pathophysiological conditions. To examines of human samples, some housekeeping genes are frequently used as internal reference, which also named endogenous control genes, such as Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase, b-actin, 18S ribosomal RNA, heat-shock protein-90, b-2-microglobulin, b-tubulin and others. However, for tree shrew, most of their sequences are still unknown. GAPDH playing an important role in both of glycolysis and nuclear functions, respectively, given that is has both glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and nitrosylase. GADPH also is an important enzyme in the process of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis, whose cycles occur in the cytoplasm. It is responsible for catalyzing the reversible conversion of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphateand inorganic phosphate into 1,3-bisphosphoglyceratewith a three-step reaction. Moverover, GAPDH has been implicated it is involved in several non-metabolic processes, including transcription activation, ER to Golgi vesicle shuttling, initiation of apoptosis, and axoplasmic transport, or fast axonal. Thereby, GAPDH was considered it is experssed in every cell, tissue, and organ. It is one 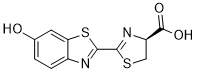 of “housekeeping” molecules that were used as an internal reference to correct the potential error of RNA/cDNA loading, and variation of reverse transcription efficiency. GAPDH is widely considered as a molecule that is expressed at relatively constant levels in most situations. However, some studies disagreed to this. In this study, we identified full-length cDNA sequence of tree shrew GAPDHgene. Using this sequence, we construct the genetic family tree and study the GAPDH expression profiles in tree shrew. These studies provide the novel genetic and proteomic knowledge of tree shrew, and the strong evidence that tree shrew can be a potential animal model to study human disorders.
of “housekeeping” molecules that were used as an internal reference to correct the potential error of RNA/cDNA loading, and variation of reverse transcription efficiency. GAPDH is widely considered as a molecule that is expressed at relatively constant levels in most situations. However, some studies disagreed to this. In this study, we identified full-length cDNA sequence of tree shrew GAPDHgene. Using this sequence, we construct the genetic family tree and study the GAPDH expression profiles in tree shrew. These studies provide the novel genetic and proteomic knowledge of tree shrew, and the strong evidence that tree shrew can be a potential animal model to study human disorders.
Locally expressed CGRP stimulated the nerves and promoted the synthesis and release of CGRP in several organs
In northeast China supports the likely occurrence of zoonotic transmission. Actions should be taken to reduce close contact between E. bieneusi-harboring pigs and susceptible human populations to reduce the spread of microsporidiosis. In conclusion, we reported the occurrence of several humanpathogenic E. bieneusi genotypes and a new genotype with zoonotic potential in healthy pigs in northeast China. Although the prevalence of E. bieneusi in livestock in China has been poorly Atractylenolide-III investigated thus far, our finding suggests that pigs could be a potential source of human microsporidian infections. Further studies are needed to fully elucidate the significance of pigs in the epidemiology of microsporidiosis in humans. Due to the high frequency of human contact with livestock in China, advice should be given to the susceptible human populations to reduce zoonotic transmission of this neglected disease. MMP-9 is a proteolytic enzyme that degrades basilar membrane and the extracellular matrix. It reportedly promotes cancer progression by increasing cancer cell proliferation, migration, invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. MMP-9 exert these effects by cleaving a diverse group of substrates, including structural components of the extracellular matrix, growth factor binding proteins, growth factor precursors, receptor tyrosine kinases, celladhesion molecules and other proteinases.However, reports conflict as to whether increased MMP-9 expression correlates with metastasis and malignancy factors.MMP-9 protein is primarily expressed in the cytoplasm of both tumor and stromal cells.In this study, its expression in matched epithelium and lymph node tissue was associated 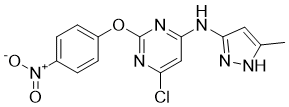 with lymph node metastasis. Stromal fibroblasts have been suggested to secrete MMP-9, which is stored and activated in tumor cells.Hence, evaluation of stromal MMP-9 expression may provide valuable information on breast cancer prognosis, especially in early carcinogenesis. A previous study showed that higher expression of MMP-9 protein was associated with lymph node metastasis,consistent with our findings. In our study, MMP-9 expression was significantly associated with LMVD and lymph node metastasis. Recent studies have demonstrated that lymphatic networks within lymph nodes expand prior to the onset of metastasis.The LMVD reflects the status of lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodeling, and when increased, improves opportunities for tumor cells to disseminate to the lymphatic system. Furthermore, it is correlated with lymphangiogenic factors, lymphatic metastasis and poor 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C prognosis in breast cancer,as confirmed by our experiments. We found that MMP-9 expression was only associated with lymph node metastasis, but not with other clinical characteristics. This implies that MMP-9 plays a major role in the lymphatic system. Thus, as a proteolytic enzyme, MMP-9 may affect the early progression of lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of breast cancer. UVB irradiation decreases the level of plasma adiponectin, but the mechanism by which UVB irradiation decreases the expression of adiponectin in ovarial adipose tissues is still unclear. UVB irradiation of the skin also increases the level of calcitonin gene-related peptidein the epidermis. CGRP is a 37 amino acid peptide produced by alternative splicing of the calcitonin-CGRP gene transcript. It is widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, skin, liver, heart, and blood vessels.
with lymph node metastasis. Stromal fibroblasts have been suggested to secrete MMP-9, which is stored and activated in tumor cells.Hence, evaluation of stromal MMP-9 expression may provide valuable information on breast cancer prognosis, especially in early carcinogenesis. A previous study showed that higher expression of MMP-9 protein was associated with lymph node metastasis,consistent with our findings. In our study, MMP-9 expression was significantly associated with LMVD and lymph node metastasis. Recent studies have demonstrated that lymphatic networks within lymph nodes expand prior to the onset of metastasis.The LMVD reflects the status of lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic vessel remodeling, and when increased, improves opportunities for tumor cells to disseminate to the lymphatic system. Furthermore, it is correlated with lymphangiogenic factors, lymphatic metastasis and poor 14alpha-hydroxy-Sprengerinin-C prognosis in breast cancer,as confirmed by our experiments. We found that MMP-9 expression was only associated with lymph node metastasis, but not with other clinical characteristics. This implies that MMP-9 plays a major role in the lymphatic system. Thus, as a proteolytic enzyme, MMP-9 may affect the early progression of lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis of breast cancer. UVB irradiation decreases the level of plasma adiponectin, but the mechanism by which UVB irradiation decreases the expression of adiponectin in ovarial adipose tissues is still unclear. UVB irradiation of the skin also increases the level of calcitonin gene-related peptidein the epidermis. CGRP is a 37 amino acid peptide produced by alternative splicing of the calcitonin-CGRP gene transcript. It is widely distributed in the central and peripheral nervous systems, skin, liver, heart, and blood vessels.
Metfromin may not work on regular tumor cells but work on stem cells
It has been shown that metformin could selectively target cancer stem cells, and act together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission in multiple cancer cell types. Metformin can also inhibit the inflammatory response associated with cellular transformation and cancer stem  cell growth. In addition, metformin can accelerate the growth of BRAF V600Edriven melanoma by upregulating VEGF-Aand promote the angiogenic phenotype in the ERalpha negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model. Overall, metformin may only have effects in preventing tumor initiation but after the cancer has been established it may not have an effect. Our data also showed that metformin exposure did not inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth, induce apoptosis or autophagy and cell cycle arrest. In agreement with in vitro, in vivo study revealed that metformin did not suppress tumor growth but AMPK activator AICAR emerged antitumor activity. Therefore, metformin might have no antineoplastic activity for CRC cells as a single agent. The anticancer effects of AICAR are mediated by the activation of AMPK and reduction of mTOR signaling. AMPK activation can suppress mTOR pathway to inhibit cell growth and proliferation. AICAR have been reported to enhance the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of local and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. AMPK activators such as AICAR provide a therapeutic strategy for hematological malignancies. First, AICAR can induce apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cellsand kill chronic myelogenous leukemiacells through PKC-dependent induction of autophagic cell death. Second, AICAR has antileukemic effects on BCR-ABL-expressing cellsand childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemiacells. Third, AICAR can induce G/S arrest and Nanog downregulation via p53 and enhance erythroid differentiation. Finally, AICAR can also induce apoptosis independently of AMPK and p53 through up-regulation of the BH3-only Benzoylpaeoniflorin proteins BIM and NOXA in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. In addition to NPC and leukemia, AICAR is involved in neural stem cell growth suppression and cell cycle arrest by down-regulating phosphoretinoblastoma protein and cyclin D. AICAR can inhibit the growth of retinoblastoma by decreasing angiogenesis and inducing apoptosisor activation of AMPK. AICAR is also demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of EGFRvIII expressing glioblastoma through AMPK pathway. Moreover, AICAR can be used in clinical trials as a cardioprotectant under ATPdepleted conditions and has been shown to be an exercise mimetic in animals. In agreement with these results, we reported that AICAR can induce apoptosis to emerge antineoplastic activity. Furthermore, AICAR enhanced the cytotoxic effect of 5-FU through AMPK activation. In conclusion, our study revealed that use of metformin alone is not associated with survival outcomes of colorectal cancer cell but AMPK activator AICAR can induce apoptosis and emerge antineoplastic activity. Furthermore, activation of AMPK might be a key cause that AICAR can enhance the cytotoxic effect of 5FU in colorectal cancer cells. The study of adipose tissue biology is becoming Praeruptorin-B increasingly important as obesity and its related comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and certain cancers, are threatening the health of a growing number of people worldwide.
cell growth. In addition, metformin can accelerate the growth of BRAF V600Edriven melanoma by upregulating VEGF-Aand promote the angiogenic phenotype in the ERalpha negative MDA-MB-435 breast cancer model. Overall, metformin may only have effects in preventing tumor initiation but after the cancer has been established it may not have an effect. Our data also showed that metformin exposure did not inhibit colorectal cancer cell growth, induce apoptosis or autophagy and cell cycle arrest. In agreement with in vitro, in vivo study revealed that metformin did not suppress tumor growth but AMPK activator AICAR emerged antitumor activity. Therefore, metformin might have no antineoplastic activity for CRC cells as a single agent. The anticancer effects of AICAR are mediated by the activation of AMPK and reduction of mTOR signaling. AMPK activation can suppress mTOR pathway to inhibit cell growth and proliferation. AICAR have been reported to enhance the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agents in the treatment of local and metastatic nasopharyngeal carcinoma. AMPK activators such as AICAR provide a therapeutic strategy for hematological malignancies. First, AICAR can induce apoptosis in B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cellsand kill chronic myelogenous leukemiacells through PKC-dependent induction of autophagic cell death. Second, AICAR has antileukemic effects on BCR-ABL-expressing cellsand childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemiacells. Third, AICAR can induce G/S arrest and Nanog downregulation via p53 and enhance erythroid differentiation. Finally, AICAR can also induce apoptosis independently of AMPK and p53 through up-regulation of the BH3-only Benzoylpaeoniflorin proteins BIM and NOXA in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. In addition to NPC and leukemia, AICAR is involved in neural stem cell growth suppression and cell cycle arrest by down-regulating phosphoretinoblastoma protein and cyclin D. AICAR can inhibit the growth of retinoblastoma by decreasing angiogenesis and inducing apoptosisor activation of AMPK. AICAR is also demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of EGFRvIII expressing glioblastoma through AMPK pathway. Moreover, AICAR can be used in clinical trials as a cardioprotectant under ATPdepleted conditions and has been shown to be an exercise mimetic in animals. In agreement with these results, we reported that AICAR can induce apoptosis to emerge antineoplastic activity. Furthermore, AICAR enhanced the cytotoxic effect of 5-FU through AMPK activation. In conclusion, our study revealed that use of metformin alone is not associated with survival outcomes of colorectal cancer cell but AMPK activator AICAR can induce apoptosis and emerge antineoplastic activity. Furthermore, activation of AMPK might be a key cause that AICAR can enhance the cytotoxic effect of 5FU in colorectal cancer cells. The study of adipose tissue biology is becoming Praeruptorin-B increasingly important as obesity and its related comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease and certain cancers, are threatening the health of a growing number of people worldwide.